- · 《中国卫生政策研究》期[04/29]
- · 中国卫生政策研究版面费[04/29]
- · 《中国卫生政策研究》投[04/29]
- · 《中国卫生政策研究》数[04/29]
中国若"躺平"代价有多大?研究模拟数据: 上亿
作者:网站采编关键词:
摘要:In addition, about 3.35 billion COVID-19 vaccine doses had been administered across the Chinese mainland, said Wu Liangyou of the National Health Commission (NHC), and nearly 757 million people, or over half of the population, had received
In addition, about 3.35 billion COVID-19 vaccine doses had been administered across the Chinese mainland, said Wu Liangyou of the National Health Commission (NHC), and nearly 757 million people, or over half of the population, had received the booster jab.此外,国家卫生健康委的吴良友表示,中国大陆共接种约33.5亿剂新冠疫苗,超过一半的人口(近7.57亿人)进行了加强针注射。
声明:转载此文是出于传递更多信息之目的。若有来源标注错误或侵犯了您的合法权益,请作者持权属证明与本网联系,我们将及时更正、删除,谢谢。
The study, led by China's Fudan University with scientists from China and the US, estimated that an Omicron wave would result in 112 million symptomatic infections, 2.7 million intensive care admissions (15.6 times the existing capacity) and almost 1.55 million fatalities between May and July in China without the country's dynamic-zero-COVID policy. The related paper was published on the website of the international journal Nature Medicine Tuesday.这项由复旦大学主导、中美科学家联合开展的研究预测,如果中国不采取“动态清零”政策,在5月至7月期间,奥密克戎毒株将导致1.12亿症状感染、270万人需要重症监护(现有能力的15.6倍),以及155万人死亡。相关论文5月10日发表在国际期刊《自然医学》的网站上。
This mathematical model on infection rates looked at the situation in China as a whole and separately in Shanghai Municipality and China's Shanxi and Shandong provinces to project the COVID-19 burden if the dynamic zero-COVID policy hadn't been adopted. It focused on cases, patients requiring hospitalization and intensive care, and deaths, using hypothetical mitigation scenarios.该感染率数学模型除了对全国平均水平进行分析外,还比较了上海、山东、山西三地的情况。预测不采取“动态清零”防疫政策的新冠感染负担。研究使用假设的新冠缓解策略进行预测,重点关注感染人数、需要住院治疗和重症监护的病例数以及死亡人数。
图表使用国家和地区流行病学家委员会(CSTE)的定义对新冠肺炎病例进行分类。Over 86% Chinese mainland seniors are vaccinated超86%的中国大陆老年人接种了新冠疫苗
图3:如果不采取“动态清零”政策,2022年3月至8月预计床位与重症监护病房资源需求情况
Based on the COVID-19 situation in Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR), the mortality rate of the elderly who complete three-shot vaccination drops as much as 74 times compared to the unvaccinated, said Zheng. Even for those who only take one shot, the death rate declines three times compared to those without vaccines.郑中伟称,按照香港特区的疫情情况,完成三剂疫苗接种的老年人死亡率比未接种疫苗的老年人死亡率下降了74倍。即使只接种一剂疫苗的人,死亡率也比没有接种过疫苗的人下降了三倍。
Zheng Zhongwei, head of vaccine research and development at the NHC, said the data shows vaccination is highly effective for the elderly to fend off severe symptoms and death when infected by COVID-19.国务院联防联控机制科研攻关组疫苗研发专班工作组组长、卫健委郑中伟表示,数据显示,接种疫苗能有效降低老年人的重症和死亡风险。
如果中国放弃严格的清零政策,将会给民众造成怎样的影响?由来自复旦大学、华山医院、美国国立卫生研究院和印第安纳大学的研究人员5月10日共同发表于《自然医学》(Nature Medicine)杂志上的模型研究显示,在“完全躺平”的情况下,奥密克戎毒株在中国的传播预计会导致155万人死亡。
转载:中国日报

图1:如果不采取“动态清零”政策,不同年龄组感染结局(中国整体、上海、山西、山东)
图2:假如不采取“动态清零”政策的住院率、重症率、死亡率
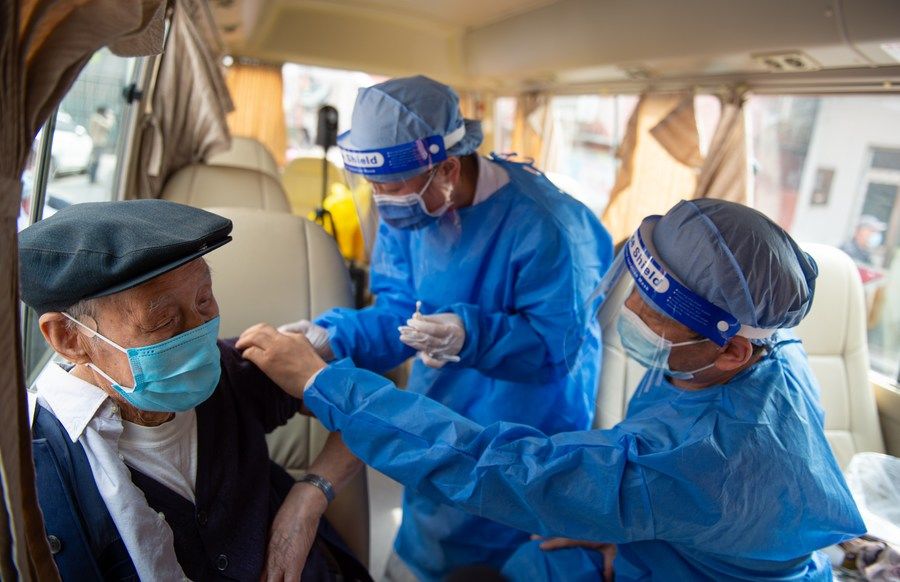
As for the senior citizens aged 60 and above – the category most vulnerable to COVID-19 – over 227 million people, or 86.23 percent of the group, had been vaccinated. Over 162 million of the Chinese seniors have received booster shots, added Wu.60岁及以上的老年人(新冠病毒最易感染人群)中,超过2.27亿人接种了新冠疫苗,占该群体的86.23%。吴良友还表示,超过1.62亿的中国老年人进行了加强针注射。
The essence of the dynamic zero-COVID approach is early detection and quick response measures to stop the continuous spread of the virus in communities to protect people's health and lives to the greatest extent.?“动态清零”的实质是早期检测和快速反应措施,阻止病毒在社区的持续传播,最大限度地保护人民的健康和生命。
文章来源:《中国卫生政策研究》 网址: http://www.zgwszcyjzz.cn/zonghexinwen/2022/0518/765.html